
The muscadine grape is a nutritional powerhouse. Like many intensely colored fruits, vegetables, and berries, the muscadine grape is a rich source of polyphenols. The skins and seeds of muscadine grapes are particularly rich in the polyphenolic compound resveratrol, which has been studied for its anti-oxidant benefits in numerous diseases, including cancer and heart disease. However, many of the health benefits of the muscadine have been linked to other polyphenolics, including ellagic acid.
New Muscadine Research at Wake Forest University School of Medicine
Links to Scientific Research Papers
Muscadine Nutritional Facts
One serving of grapes is about 1/2 cup, or 16 grapes. That amount of muscadines has: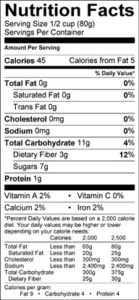
- 55 calories
- 0.78 grams of protein
- 0.45 g of fat
- 13.37 g of carbohydrate
- 3.37 g of fiber
- They are also about 84 percent water.
They are fat free, cholesterol free, sodium free, an excellent source of manganese, and a good source of fiber.
Muscadine Polyphenols
Polyphenols are highly complex chemicals found in plants that provide multiple health benefits. Years of research have shown that polyphenols from foods support the function of brain, heart, liver, joints, muscle recovery, and other organs. As anti-oxidants, these phytonutrients support the body’s cellular function and recovery from normal metabolism, and reduce oxidative stress and inflammation associated with many disease states. Muscadine grapes contain particularly high concentrations of polyphenols as compared to other grape varieties. The highest concentrations of these healthful phytonutrients are in the skins and seeds of the grapes.
The muscadine’s polyphenols include both resveratrol and ellagic acid, two anti-oxidants that are also found in red wine, pomegranate and berries. Resveratrol is a well-researched anti-oxidant that extended the lifespan of animals, improved the metabolic function of the energy-producing mitochondria, and possesses a number of beneficial activities when consumed. Ellagic acid and gallic acid, plus the polyphenolic tannins from which they are derived during ripening and processing, are potent anti-oxidants that have metabolic, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities.
Muscadines also contain flavonoids such as anthocyanins and quercetin, which give muscadines their purple-red or yellow hue, respectively. Scientific studies, such as cell culture experiments, animal models, and human clinical trials, show that anthocyanidins and anthocyanins possess anti-oxidative and anti-microbial activities, improve visual and neurological health, and protect against various non-communicable diseases. Quercetin is a more potent anti-oxidant than vitamin C, vitamin E, or beta carotene.
